4.2 Api Management (Gravitee)#
The Developer Portal is where the Orchestra Cities APIs are registered, and the policies defined. The following section describes how these APIs are registered in the Developer Portal and how policies and Oauth2 authorization are handled.
4.2.1 The Authorization flow#
-
The user requests a token for the client API from Keycloak. The token comes from a public client in Keycloak, so no secret is required to obtain a token. It's worth reminding that the public clients set up in Keycloak will limit what the given tokens enable users to do, such as user management operations. The user requests a specific scope with the request (e.g. entity:read). A list of scopes is available in the Keycloak Configuration section of this documentation.
-
When then token is used, it is validated against Keycloak's confidential client (the resource-server client). The operation being attempted (e.g. creating an entity under Tenant X and Servicepath Y) is allowed if the correct scope is present and the Tenant and Servicepath allow it.
-
The authorisation is carried out according to the contents of the token.
4.2.2 Protecting an API#
To set up and protect an API through the Gravitee Developer Portal, one must do two things after registering the API: defining an Oauth2 resource to authenticate and authorize users, and define for each path of the API which policies should be applied.
4.2.2.1 Oauth2 Resource#
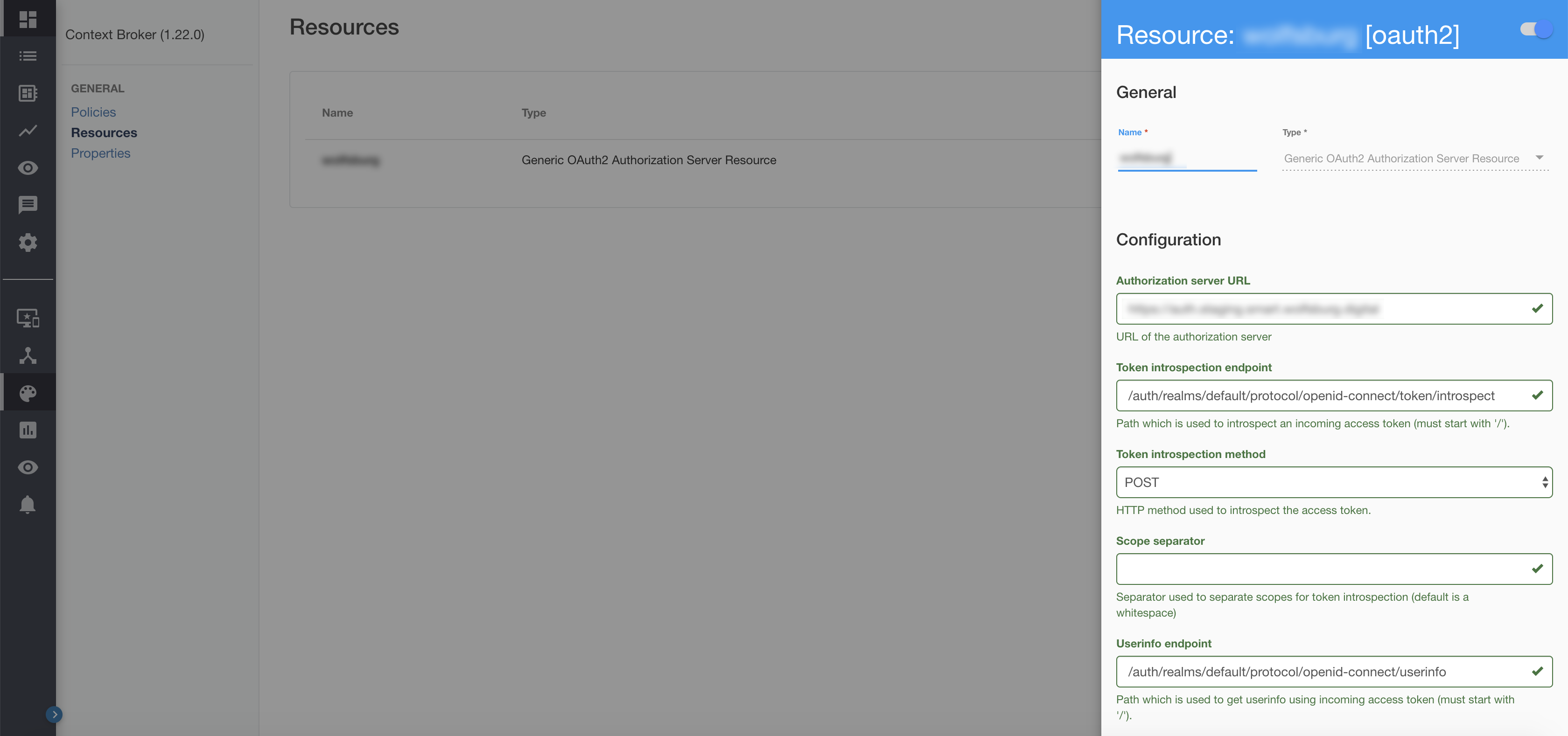
Within the Developer Portal, for each API, Oauth2 access to Keycloak is configured as a Generic Oauth2 Authorization Server Resource. This is done to check tokens against the confidential client resource-server in Keycloak, where scopes are listed.
The configuration contains:
- Authorization Server URL: The Keycloak URL
- Token introspection endpoint: /auth/realms/default/protocol/openid-connect/token/introspect
- Token introspection method: POST
- Userinfo endpoint: /auth/realms/default/protocol/openid-connect/userinfo
- Userinfo method: GET
- Client Id: resource-server
- Client secret: The secret of the resource-server client
- Authorization header: Authorization
- Authorization scheme: Basic
- Token query param name: token
- Form param name: token
4.2.2.2 Policies#
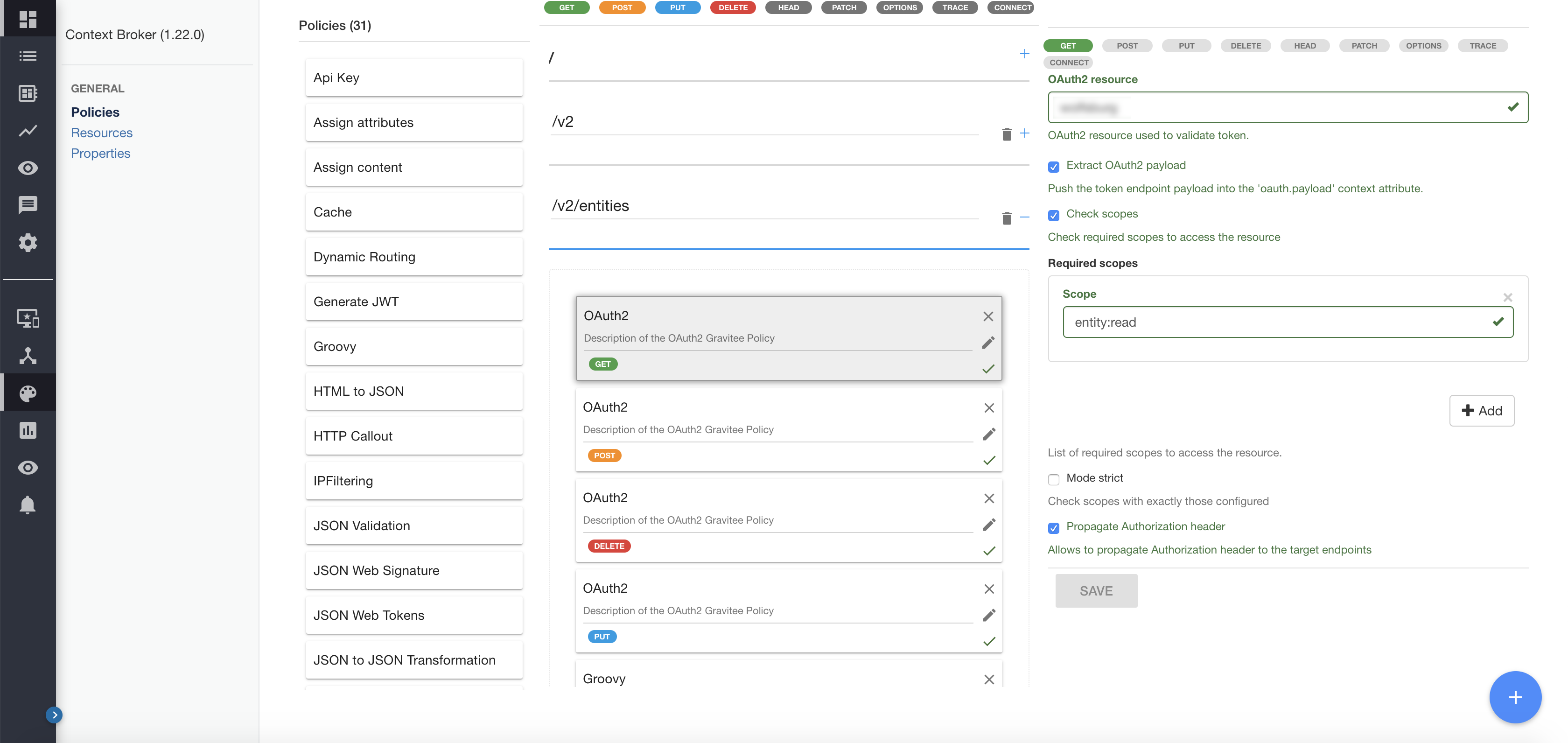
For each API endpoint, policies are in place for each operation. This enables API owners to decide exactly what scopes are required for users to perform different operations, whether is accessing, editing, creating or deleting resources. See the Keycloak Configuration section for more details on client scopes.
Policies follow a basic syntax of resource:operation, so for the /entities endpoint of the Context Broker for example we have:
- GET requires scope entity:read
- PUT requires scope entity:write
- POST requires scope entity:create
- DELETE requires scope entity:delete
In addition, there's a policy in the form of a Groovy script in place for all
operations that checks the Oauth payload for the Tenant and ServicePath,
ensuring the operation being performed is authorised.
The script:
// The following scripts reads the token payload, extract the information about
// tenants and service paths, and authorises the user if the requested tenant and
// service paths are present. Returns 401 otherwise.
import io.gravitee.policy.groovy.PolicyResult.State
import groovy.json.JsonSlurper
import groovy.json.JsonOutput
def jsonSlurper = new JsonSlurper()
def authorised = false;
def content = null;
if(context.attributes['oauth.payload']){
content = jsonSlurper.parseText(context.attributes['oauth.payload']);
}
if (request.headers.containsKey('fiware-Service') && content) {
def service = request.headers.get('fiware-Service').get(0)
if (content['fiware-services'].get(service)){
def serviceList = content['fiware-services'].get(service)
if (request.headers.containsKey('fiware-ServicePath')) {
def servicePath = request.headers.get('fiware-ServicePath').get(0)
authorised = serviceList.any{servicePath.startsWith(it)}
}
}
}
if (authorised == false) {
result.state = State.FAILURE;
result.code = 401;
result.error = '{"error":"Missing authorisation for specified fiware-service and fiware-servicePath","code":"UNAUTHORISED"}';
}